3. Using the DEVKIT#
This chapter provides instructions for using HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX, such as booting and how to configure and use I/O peripherals (e.g. serial console, Ethernet).
3.1. HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX Overview#
An overview of the available connectors and devices on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX is shown below.
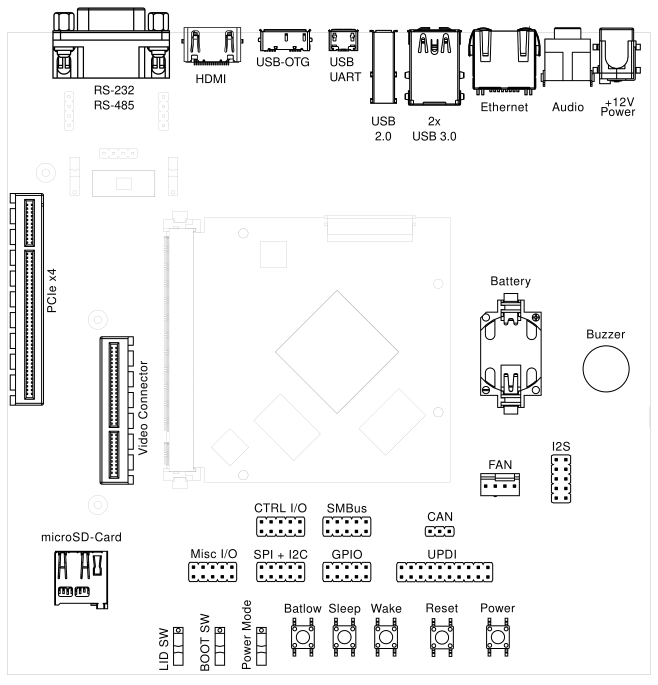
Fig. 3.1 HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX with TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7#
3.2. Power Supply#
HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX can operate with a single 12V DC power supply. The 12V DC connector is highlighted below.
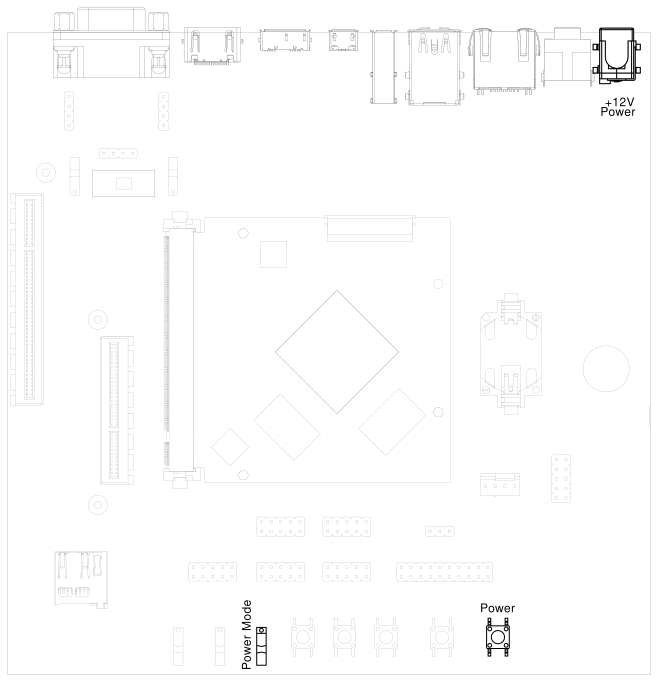
Fig. 3.2 12V Power connector#
Power can be controlled manually from the carrier board using the Power control buttons
and switches, located on the lower right side of the carrier board (see Section 3.1 HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX Overview).
Depending on the setting of Power Mode (Normally On / Normally Off) switch, HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX will boot as soon as it receives power.
3.4. CPU Fan#
Intensive applications require a CPU fan, the fan connector is located next to the bottom right corner of the Q7 expansion area.
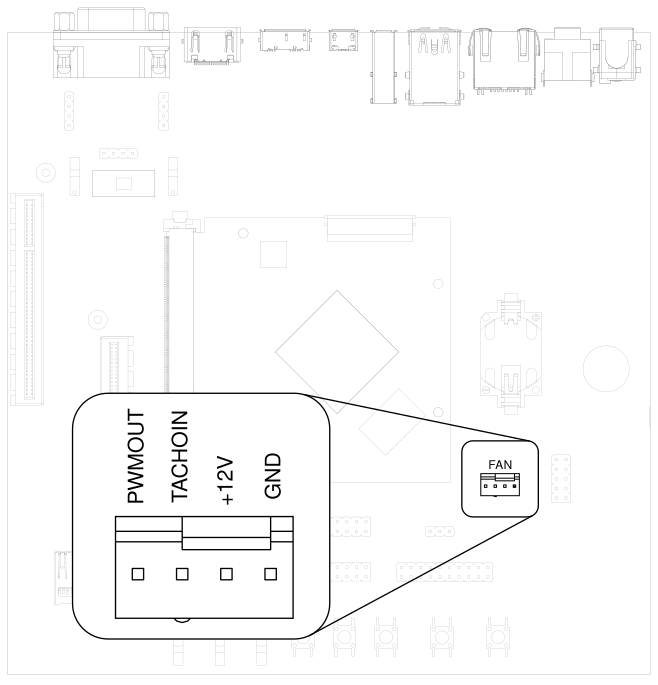
Fig. 3.3 Fan connector#
Note
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 is designed for highly intensive tasks, so it normally emits heat. In normal use-cases and normal conditions, TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 emits heat while operating.
3.5. Boot Order#
The used boot order of TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 depends on the value of the BIOS_DISABLE# signal.
On HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX this signal can be set using a slider switch (BOOT SW), with the two positions
labeled Normal Boot, and BIOS Disable.
As shown in the table below, the BIOS Disable position disables the eMMC storage device:
Normal Boot |
BIOS Disable |
|
|---|---|---|
1 |
eMMC storage |
SD card |
2 |
SD card |
USB loader |
3 |
USB loader |
If no bootloader is found on any storage device, TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 module will go into USB loader mode, showing up as a USB device on the USB-OTG port.
The electrical state of the BIOS_DISABLE# signal for both slider positions is shown below:
Slider Position |
|
|---|---|
Normal Boot |
Floating (on-module pull-up to 3.3V) |
BIOS Disable |
GND |
3.6. USB Serial Console#
HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX contains an on-board Silicon Labs CP2102N USB-serial converter.
Connect the included Micro-USB cable to the Micro-USB jack labeled USB-UART Bridge:
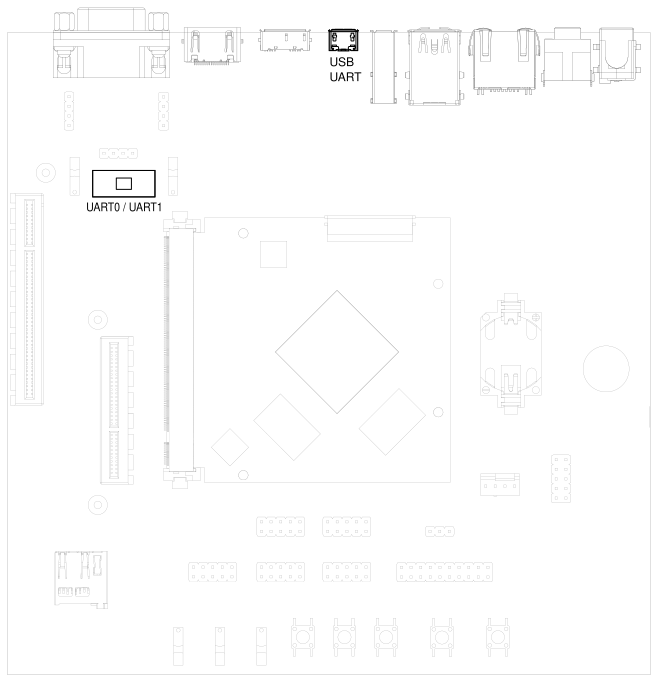
Fig. 3.4 USB UART#
The serial converter does not require additional drivers on Windows and Linux.
For macOS, drivers are available from Silicon Labs: https://www.silabs.com/products/development-tools/software/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 has two external UARTs:
UART0 is, by default, used for the serial console for interactive login.
UART1 is unused by default and can be freely used for machine-to-machine communications or other purposes.
The switch UART0 / UART1 cross-switches UART0 and UART1 between the RS232 / RS485 jack and the onboard
USB-serial converter:
Switch Position |
|
USB-serial converter connected to: |
|---|---|---|
|
UART0 (interactive console) |
UART1 |
|
UART1 |
UART0 (interactive console) |
For interactive login through the USB-serial converter, make sure the switch is on the
UART1 position.
Note
UART1 is the name of the UART exposed on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX. It is actually
connected to the UART5 controller on the RK3588 SoC.
UART0 on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX is connected to the UART2 controller on the RK3588 SoC.
Picocom can be used to connect via the serial line (assuming the USB-serial converter is USB0):
picocom -b 115200 /dev/ttyUSB0
Note
Make sure to disable software flow-control (XON/XOFF). Otherwise, serial input may not be recognized.
After system boot-up, the login console appears on the terminal:
RK3588-Q7 login:
You can log in as root with password root.
3.7. RS-232 and RS-485#
To connect via RS-232 or RS-485, connect to the RS232 / RS485 jack on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX.
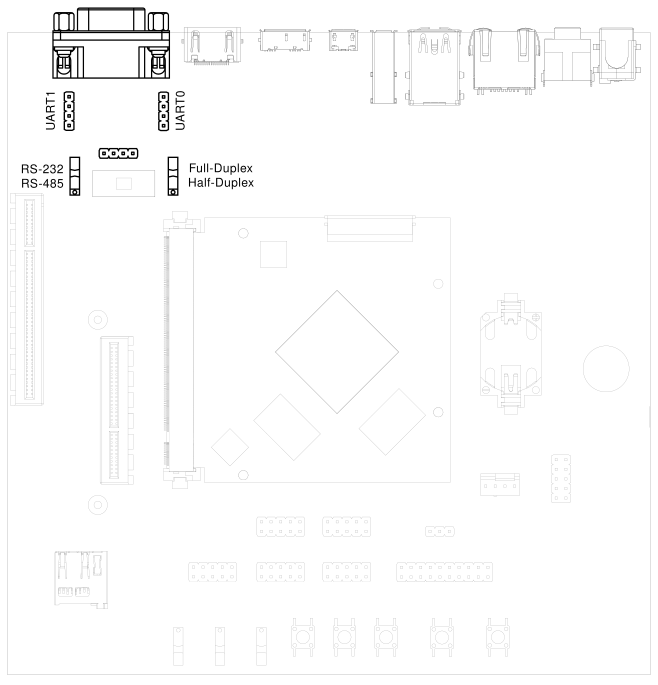
Fig. 3.5 RS-232 connector#
The switch labeled RS-232 / RS-485 selects between RS-232 and RS-485 mode on the jack.
In RS-485 mode, the switch labeled Full Duplex / Half Duplex selects full- or half-duplex mode,
respectively. It has no effect in RS-232 mode, which is always full-duplex.
3.8. TTL UART#
UART0 and UART1 are also available through the pin headers P12 UART0 and P30 UART1
next to the RS232 / RS485 jack. The signal level is 3.3V.
3.9. Ethernet#
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 has built-in Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbit/s) routed to a standard RJ-45 jack on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX.
The SD card that is shipped with the DEVKIT is configured to automatically retrieve an IP address via DHCP and provides SSH login on port 22.
3.10. SD-Card#
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 supports UHS SD cards and maximum writing speed on the SD card is 50 MB/s. The practical writing and reading speeds depend on the capabilities of the inserted SD card.
3.11. USB Interfaces#
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 provides four USB ports:
1x USB 3.0 OTG
2x USB 3.0 Host
1x USB 2.0 Host
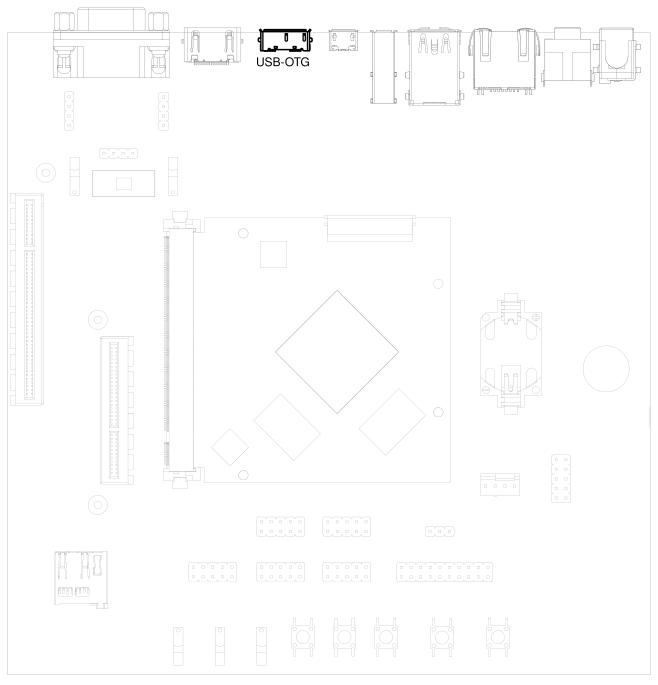
Fig. 3.6 USB 3.0 OTG port (dual-role port: can be used as a host or device interface)#
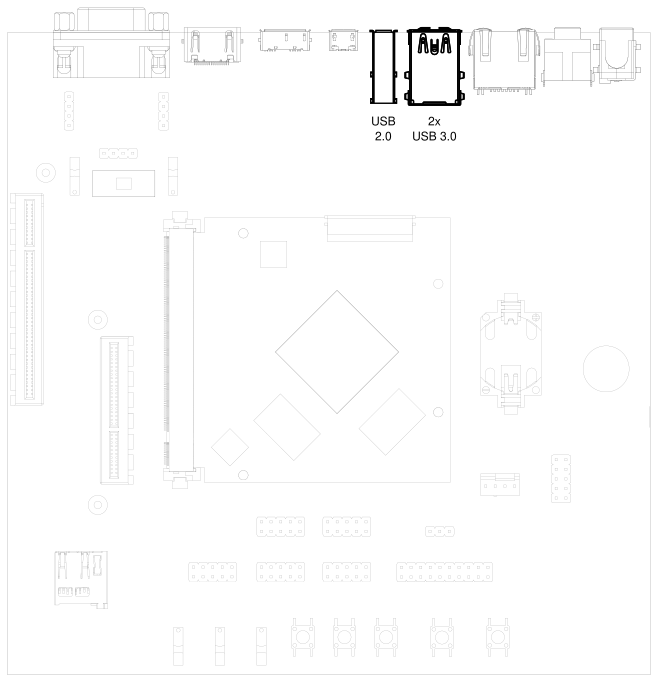
Fig. 3.7 USB 2.0 host port (vertical) and 2 x USB 3.0 host ports (stacked horizontal)#
3.11.1. Connecting an External USB Drive#
To connect a USB drive, plug it into one of the USB ports. The system should recognize the drive immediately. Check the kernel log to find the device name:
dmesg -f
You will be able to mount its partitions (assuming mapping to /dev/sdb1):
mkdir /mnt/usb1
mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/usb1
ls /mnt/usb1
3.12. Display and Camera#
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 supports display output on the eDP0/LVDS A interface and the camera on the eDP1/LVDS B interface.
For MIPI-DSI and MIPI-CSI, the Qseven LVDS pins are used. Those pins are routed to the
Video connector. This expansion slot uses a PCIe connector as mechanical
connection, which allows easy development of adapter boards for various
different display types.
Qseven Port |
Function |
|---|---|
eDP0/LVDS A |
MIPI-DSI |
eDP1/LVDS B |
MIPI-CSI |
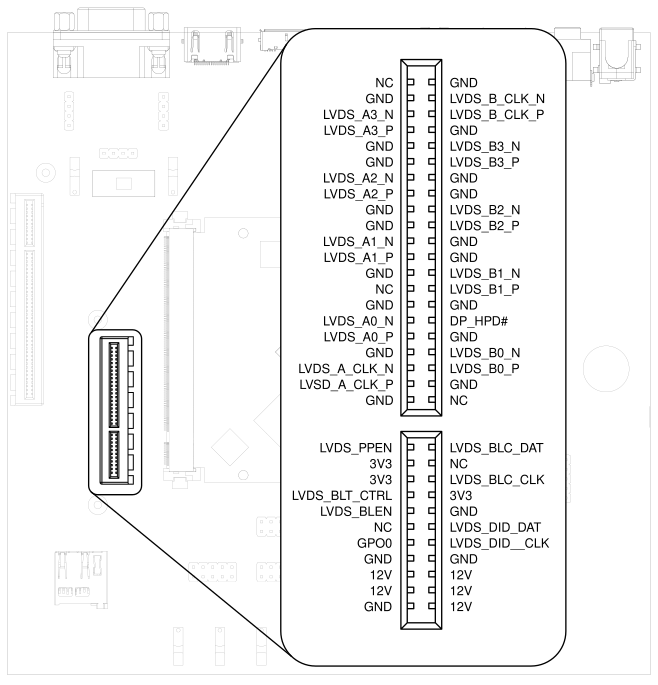
Fig. 3.8 Video connector pinout#
3.13. FFC Expansion Connectors#
Fig. 3.9 Top FFC expansion connector. The second connecter is right below on the bottom of the PCB.#
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 has two FFC connectors that enables it to support multiple cameras..
3.14. RTC#
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 contains a real-time clock (RTC) on-module.
Note
This functionality is implemented in the optional Mule companion controller (see Section 9.5.3 Companion Controller).
The RTC is read by the kernel on boot-up and used to set the system clock.
To check the RTC value, use hwclock:
$ hwclock
Thu 20 Oct 2022 01:49:20 PM CEST -0.826662 seconds
The RTC will be automatically set to the system clock on shutdown, so you can set the system clock using the date command and reboot to update the RTC:
date --set 2022-10-22
date --set 04:12:33
You can also update the RTC immediately, again with hwclock:
hwclock -w
3.15. SPI and I2C#
SPI and I2C interfaces are both available on the pin header labeled SPI+I2C+1-Wire.
TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 does not support 1-Wire.
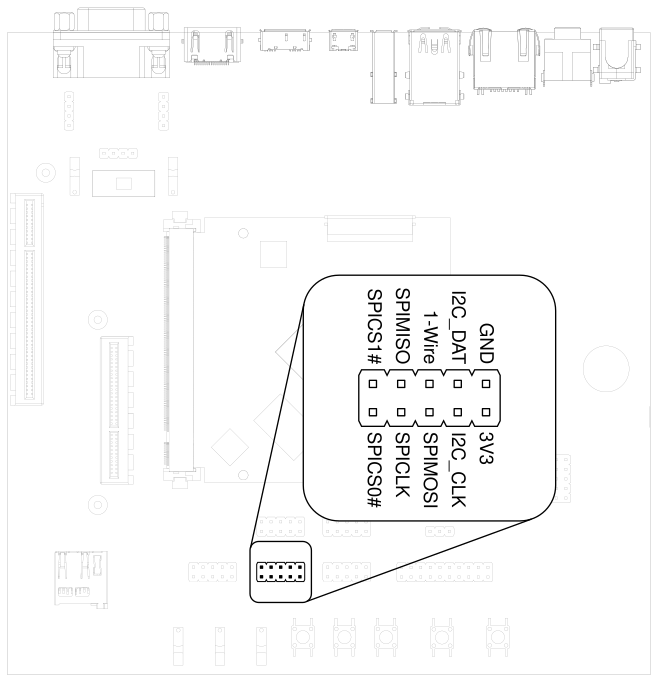
Fig. 3.10 I2C and SPI header#
Additional I2C buses are available on the SMBUS header.
(shown in thin font in Fig. 3.11).
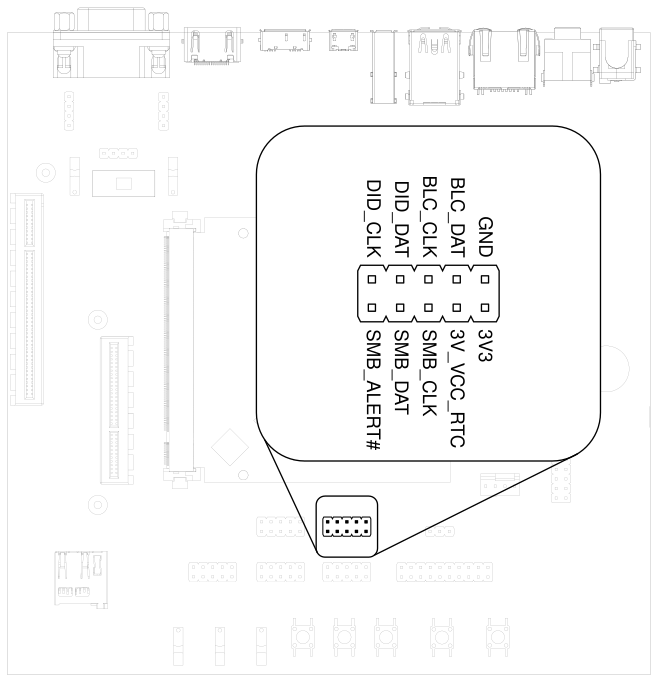
Fig. 3.11 SMBUS header#
For I2C, the i2c-tools package is available in Debian:
apt-get install i2c-tools
3.15.1. Linux I2C Bus Numbering#
Linux identifies each I2C bus by a bus number. The table below shows the mapping between Q7 names, Linux bus number and HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX header.
Q7 signal |
Linux bus |
connections/headers |
|---|---|---|
Q7_I2C_CLK, Q7_I2C_DAT |
5 |
|
Q7_SMB_CLK, Q7_SMB_DAT |
8 |
|
Q7_HDMI_CTRL_CLK, Q7_HDMI_CTRL_Dat |
|
|
LVDS_DID_CLK/GP2_I2C_DAT, LVDS_DID_CLK/GP2_I2C_DAT |
6 |
“ |
LVDS_BLC_CLK, LVDS_BLC_DAT |
1 |
“ |
The FFC expansion connector provides additional I2C buses:
FFC signal |
Linux bus |
connections/headers |
|---|---|---|
I2C4_SCL_M4, I2C4_SDA_M4 |
4 |
P2 FFC connector Pins -> (18-19) |
I2C3_SCL_M0, I2C3_SDA_M0 |
3 |
P3 FFC connector Pins -> (18-19) |
I2C2_SCL_M3, I2C2_SDA_M3 |
2 |
P2 FFC connector Pins -> (23-24) |
The other I2C buses (as reported by i2cdetect -l) are internal to the
module and not routed to external connectors.
3.16. GPIOs#
Eight GPIOs are provided on the pin header labeled GPIO.
The location on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX is displayed below:
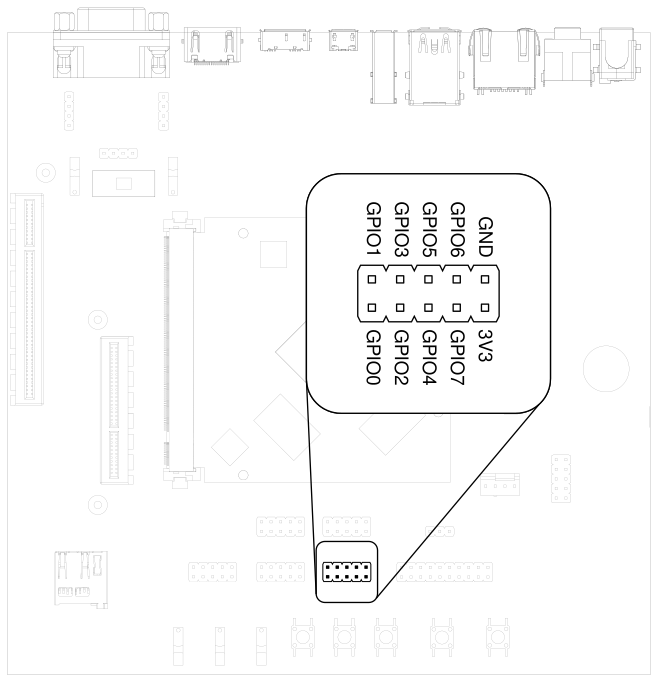
Fig. 3.12 GPIO header#
The GPIO numbers printed on the carrier board refer to numbers used in the Qseven specification.
They are different from the ones used in Linux via /sys/class/gpio.
see (Section 9.6 Using GPIOs).
3.17. Audio#
HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX provides two audio connectors for input and output.
Line-in is on top and Headphones is on bottom of the audio connector.
Note
The codec on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX only supports a sample rate 48kHz . This restriction only applies to this specific codec on HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX.
The I2S bus on TIGER SOM-RK3588-Q7 supports a sample rate up to 192kHz.
Additionally, an expansion connector for I2S audio is available on the bottom row of the carrier board:
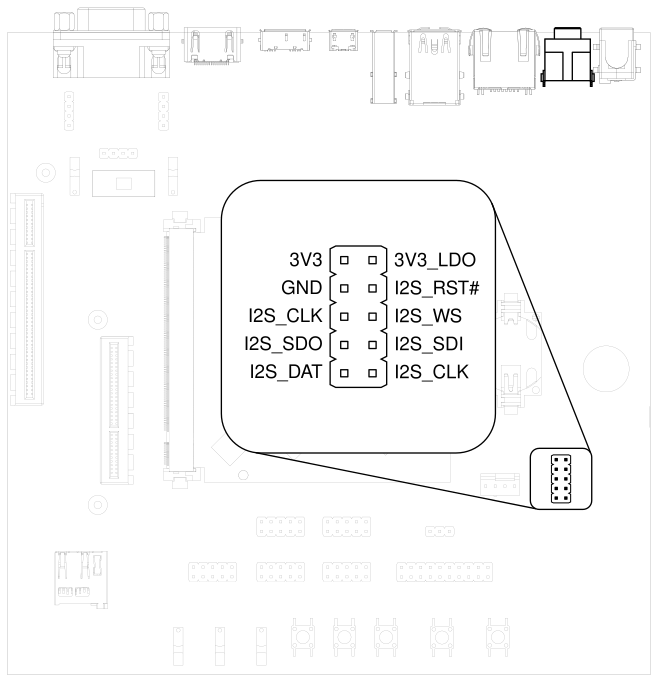
Fig. 3.13 Audio jacks and I2S header#
3.18. CAN Bus#
HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX provides a CAN connector on the bottom row.
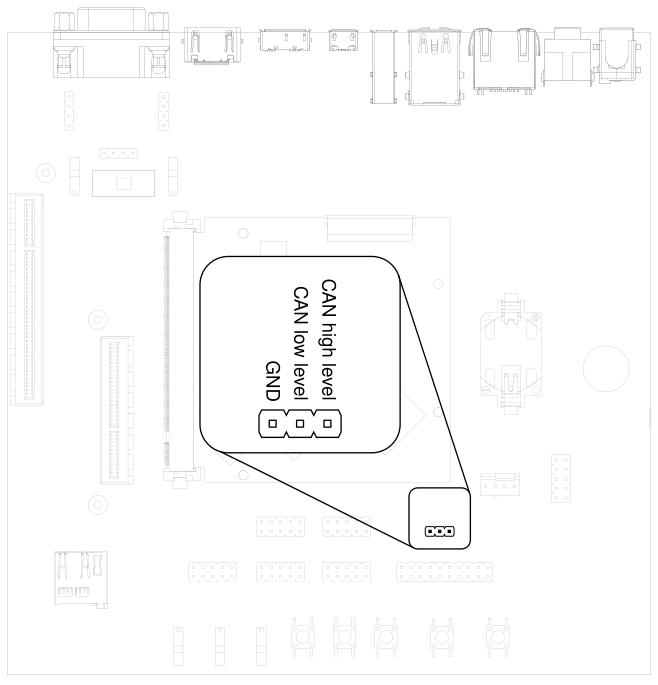
Fig. 3.14 CAN header#
3.19. CTRL I/O Connector#
HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX provides signals for watchdog trigger in- and output, SoM PMIC power-on input, reset and external display power enable.
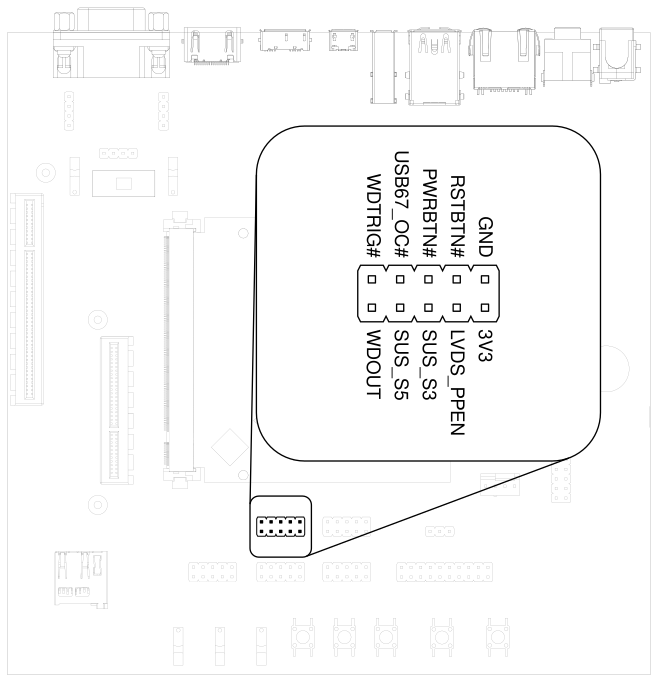
Fig. 3.15 CTRL I/O header#
3.20. MISC Connector#
HAIKOU CB-MINI-ITX provides signals for thermal overheat of external hardware and the processor, utility signals for SD and GPIO0.
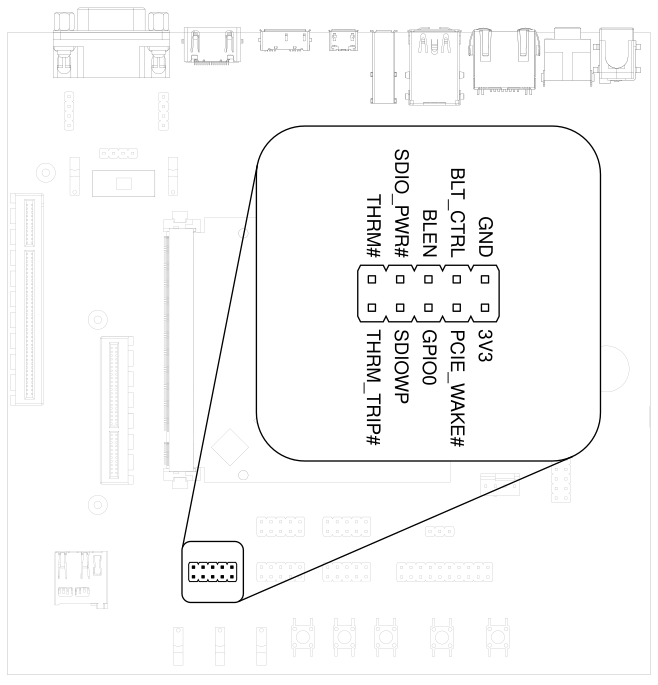
Fig. 3.16 MISC header#